Credit Reports and Credit Scores
A credit report is the list of credit activity assigned to an individual. When payments are made on a home or credit card, that information is recorded by the business and may be reported to one or more credit reporting companies. These companies combine the reported information into a credit report.
A credit report for an individual may include:
- The businesses where the individual has a loan or credit
- How often payments are made on time and the amount paid
- The amount for loan or credit limits for credit card
- Any missed or late payments
Credit scores are related to but differ from credit reports. Credit scores are created by formulas that use data in credit reports to calculate a number and grade an individual's ability to pay bills. The higher the number, the better the credit score. The higher the credit score, the more likely a borrower will receive better-than-average interest rate.
| Credit Score Range | Quality Rating | % of People |
|---|---|---|
| 800-850 | Exceptional | 21% |
| 740-799 | Very Good | 25% |
| 670-739 | Good | 21% |
| 580-669 | Fair | 17% |
| 300-579 | Very Poor | 16% |
5 Common Factors of your Credit Score
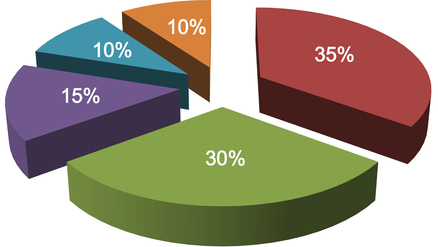
The five common factors that determine a credit score are listed below, in order of importance.
PAYMENT HISTORY (35%)
Paying debt on time (and in full) has the greatest positive impact on your credit score. Late payments, judgements, and charge-offs have a negative impact.
- Pay your bills on time, every time.
- Consider setting up automatic bill payments.
OUTSTANDING BALANCES (30%)
This is a ratio that determines the difference between the outstanding balance and the available credit. Experts agree to keep your balance at no more than 30 percent of your total limit.
- Don’t “max out” or even get close to your credit limit.
CREDIT HISTORY (15%)
Credit scores are based on experience over time; the longer you’ve had an established credit line, the better.
- Keep credit lines open as long as reasonably feasible.
TYPES OF CREDIT (10%)
A mix of mortgages, debit and credit cards, and auto loans is more beneficial than having many accounts in one type of credit.
- Apply for a CD secure, savings secure, or other line of credit to increase your credit diversity.
INQUIRIES (10%)
Recent credit activity is an indicator of your dependency on credit. If there are multiple inquiries over a short timeframe, it will negatively impact your score.
- Only apply for credit that you need.
Did you know?
Federal law entitles you to a FREE copy of your credit report from the credit reporting companies every 12 months. (You can request reports more frequently for a nominal fee.)
Visit www.AnnualCreditReport.com to get your free credit report. You may also request your credit report by phone or mail. Check your credit report regularly to make sure the report is correct.
Contact Us
For more information about how your credit score affects qualifying for a home loan, give us a call at 801-409-5000 or find a loan officer.






